low end tidal co2 range
Per moderate sedation monitoring policy. End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring ETCO2 has clinical uses far beyond solely determining hypo- or hyperventilation.

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.

. All reports to physicians respiratory therapy or RRT must be documented in the EMR. This prospective cross-sectional s. Hence that persons capnography will show a very low end-tidal CO2 level but the alveolar and arterial CO2 pressures will be much higher and increasing in time.
This is a major respiratory symptom. But ETCO2 can also provide valuable information on the adequacy of cardiac perfusion. The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle.
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. It was recently suggested that low end-tidal carbon dioxide ETco2 might be a marker of anaphylaxis Ring and Messmer grades III to IV immediate hypersensitivity reactions in hypotensive. Artour Rakhimov Alternative Health Educator and Author - Medically Reviewed by Naziliya Rakhimova MD.
Savastano S et al. Cross-sectional associations between ETCO2 and PaCO2 were examined in the study. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign.
The normal range of 35 to 45mmHg. However EtCO2 is an extremely powerful surrogate for endotracheal tube ETT P osition CPR Q uality R eturn of spontaneous. Chest compression provider tiring end-tidal CO2 value diminishes over time.
End tidal CO 2 EtCO 2. Murphy RA Bobrow BJ Spaite DW et al. Like pulse oximetry before it alerting us to changes in oxygenation end-tidal CO2 monitoring or ETCO2 is rapidly becoming an additional vital sign.
Raising the rate or the tidal volume as well as increasing T low will increase ventilation and decrease CO2. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. It is the measurement of CO2 at the completion of exhalation and roughly correlates to the CO2 present in arterial blood.
ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. For a person with normal lungs the difference between end tidal and Paco2 can vary between 5-8mmHg depending on the book your reading. If a person holds his breath that persons body accumulates CO2 and its etCO 2 is going to be zero.
PCA pump is discontinued b. If EtCO2 level is lowundetectable can be explained by 1 pulmonary blood flow is low largemassive PE 2 pulmonary exhaled air is low status asthmaticus 3 poor offloading of C02 to lungs pulmonary edema NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor.
Definition of Low CO2 hypocapnia Hypocapnia hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia is defined as a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. - Updated on September 13 2020. The objective of the present study was to measure PETCO2 during well-controlled very low blood flow rates under conditions of constant minute ventilation.
78 Nitrogen 21 Oxygen 1 CO2 and other gases Exhaled gases. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords.
IV narcotics discontinued d. Measuring end-tidal CO2 in cardiac arrest patients is helpful for confirming tracheal tube placement assessing the effectiveness of chest compressions predicting likelihood of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC in that a persistently low ETCO2 tends to predict death whereas a high or rising ETCO2 is associated with a higher chance of ROSC. Ten anesthetized intubated and mechanically ventilated swine.
Sudden increase in end-tidal CO2 return of spontaneous circulation. Total pressure of a gas is the sum of the partial pressures of the gas Expired CO2 measured PetCO2 mmHg in waveform Percentage Normal Levels PaO2 85-100mmHg PaCO2 35-45mmHg Percentage vs. In addition the partial pressure of end-tidal CO2 PETCO2 during extremely low cardiac output has not been reported.
Persistently low end-tidal CO2 check quality of compressions check ventilation volume if persistent may be a. 6 hours after continuous epidural infusion is discontinued c. Perioperative hypersensitivity reactions may be difficult to diagnose during general anesthesia.
Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function. Can the value of end tidal CO2 prognosticate ROSC in patients coding into emergency department with an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. 11172009 4 Measuring End Tidal CO2 Daltons Law.
To modify CO2 content in blood one needs to modify alveolar ventilation. The normal values are 5. Association between prehospital cpr quality and end-tidal carbon dioxide levels in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest.
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a measure of metabolism perfusion and ventilation. So the short answer is you are right about the ranges 35-45 but that. End tidal Co2 ranges vary slightly from actual PaCo2 and can be affected by many factors depending on the condition of the patients lungs.
High quality CPR consistent waveform and end-tidal CO2 20 kPa. End-Tidal CO2 in Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation. This effect could also be understood from the viewpoint of CO2 accumulation.
In the ED we typically think of a EtCO2 as a marker of perfusion and ventilation. End Tidal CO 2 sampling Ventilatory function minute ventilation decreases and therefore CO2 increases in a A dead space gasno CO2 B mixed gasrising CO2 C alveolar gasCO2 plateau D inspiration no CO2 The monitor will continuously read the CO2 level in or mm Hg and display the peak CO2 value ETCO2 and respiratory rate. Current guidance recommends an end- tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 of 4045 kPa 300 338 mm Hg to achieve a low- normal arterial partial pressure of CO2 PaCO2 and reduce secondary brain injury.
MmHg Relate to the air we breath. We routinely use ETCO2 to provide information on ventilation. To do this the tidal volume or the respiratory rate may be tampered with T low and P Low in APRV.
End-tidal carbon dioxide and defibrillation success in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. This non-invasive monitor can give valuable information about cardiac output perfusion and ventilation. Postinduction hypotension is the most common sign but is not specific.
We aimed to determine the value of sidestream end-tidal carbon dioxide SS-ETCO2 measurement in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease COPD in the emergency department. ETC02 monitoring may be discontinued when.
The Normal Capnograph Waveform Deranged Physiology

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table
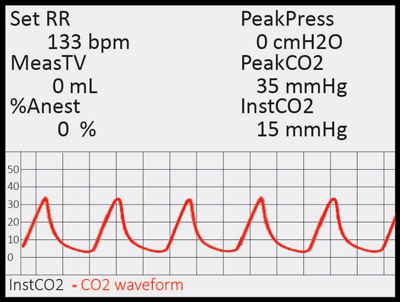
Capnoscan End Tidal Co2 Monitor Kent Scientific

End Tidal Co2 Emergency Medicine Icu Nursing Paramedic School

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Pdf Applications Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Monitoring In Emergency Department A Narrative Review Semantic Scholar

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation
